Clinical comparison of foreign body removal procedures using rigid bronchoscopy, fiberoptic bronchoscopy, and flexible electronic bronchoscopy
Jul 08, 2025
Bronchial foreign bodies are a common emergency in pediatrics. Clinically, bronchoscopy techniques are typically used to remove the foreign bodies. Currently, the three main bronchoscopy techniques each have their own characteristics, and among them, the flexible bronchoscopy shows unique clinical value in pediatric patients. This article conducts a clinical application analysis of all three bronchoscopy techniques, and the clinical application of the flexible electronic bronchoscope from Mole Medical is particularly prominent.
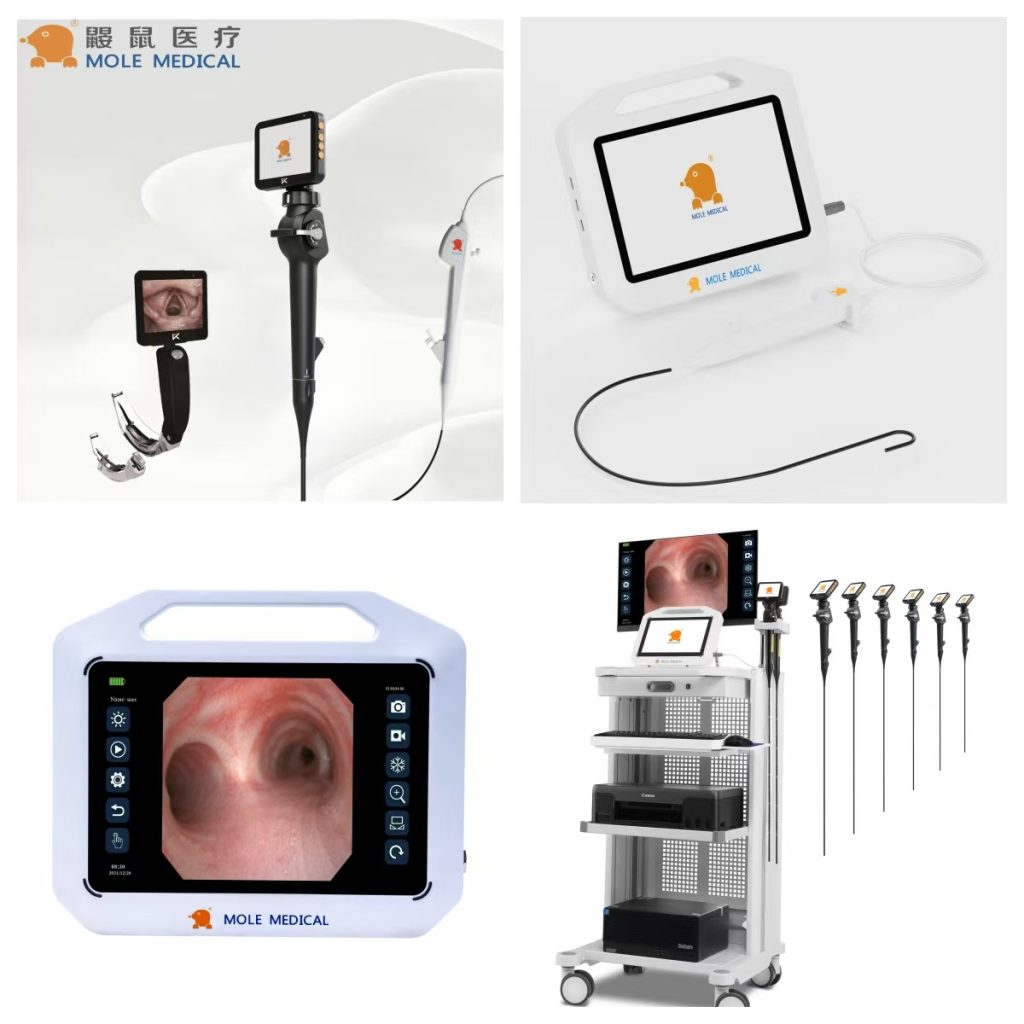
The rigid bronchoscopy, as a traditional technique, has the advantage of a large operating space, making it convenient for handling complex foreign bodies. Its rigid structure can maintain the patency of the airway, and the working channel allows the use of various retrieval instruments. However, the inability of the mirror body to bend limits the exploration of the distal bronchi and requires adjusting the head and neck position of the child during operation, increasing the risk of airway injury. Clinical data show that the postoperative complication rate of rigid bronchoscopy is relatively high, especially when dealing with peripheral bronchial foreign bodies, it has certain limitations.
Fiberoptic bronchoscopy has achieved significant breakthroughs in technology. Its flexible mirror body can explore more distal bronchi, improving the detection rate of deep foreign bodies. The optical fiber conduction system provides a relatively clear view. However, this technology requires high operator skills, and an unskilled operation may lead to an extended operation time. Additionally, the working channel of the fiber optic is relatively narrow, and its efficiency is limited when dealing with larger foreign bodies or when there is a lot of secretion.
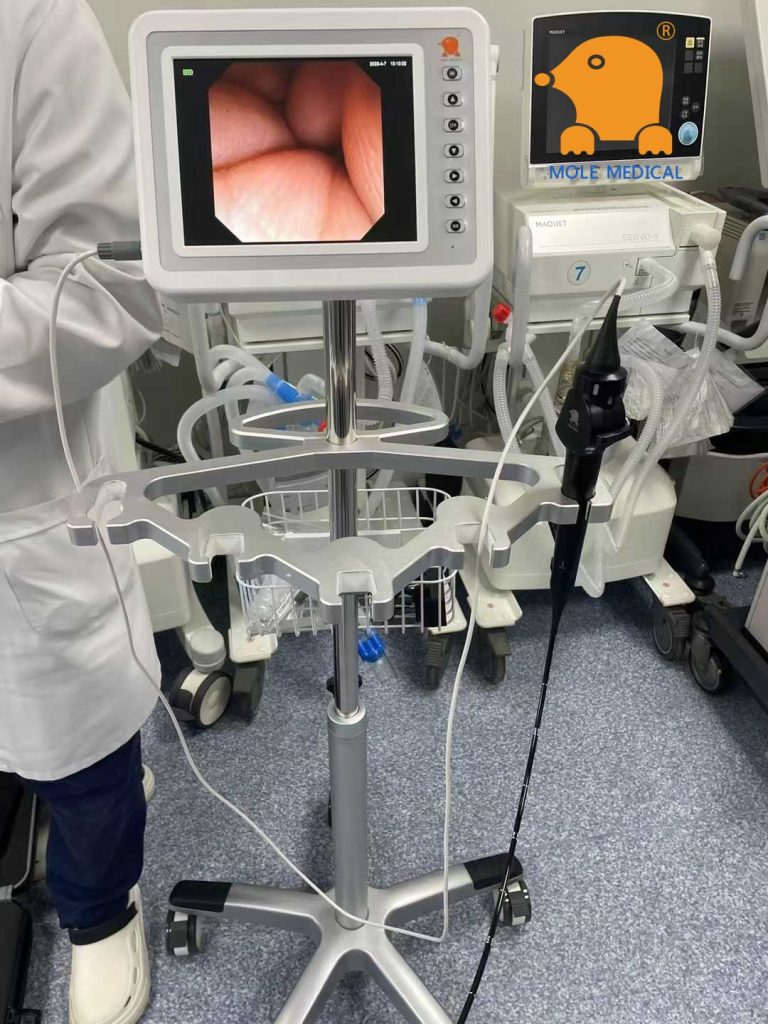
In contrast, the flexible electronic bronchoscopy combines multiple technical advantages. The electronic bronchoscope from Mole Medical’s high-definition CMOS imaging system provides high-definition vision, and the flexible mirror body design combines flexibility in exploration. Specifically, it is manifested as: (1) a wide range of upper and lower bending angles, which can reach most bronchial segments; (2) multiple specifications of mirror body diameters suitable for pediatric airways; (3) independent working channels supporting simultaneous aspiration and instrument operation. Clinical studies have shown that the flexible bronchoscopy maintains a comparable one-time removal success rate with other techniques while reducing the postoperative complication rate by 30%-40%.
In terms of anesthesia management, there are also differences among the three techniques. Rigid bronchoscopy requires general anesthesia and a deeper level of anesthesia; fiberoptic bronchoscopy can be operated under sedation, but the risk of child movement is higher; the flexible bronchoscopy provides more flexible anesthesia options, allowing for either general anesthesia or moderate sedation combined with local anesthesia for the operation, which is particularly important for children with other diseases. In addition, perioperative management is a key factor affecting the treatment outcome. After rigid bronchoscopy surgery, close observation of airway edema is required; after fiberoptic bronchoscopy operation, attention should be paid to complications such as pneumothorax; while the flexible bronchoscopy has a smaller trauma and simpler postoperative management, allowing for faster recovery of the child. Clinical statistics show that the average hospital stay of children using the flexible bronchoscopy is shorter by 1-2 days compared to the other two techniques.
From the perspective of technological development, flexible bronchoscopy is still undergoing continuous innovation. The latest model has a mirror body diameter further reduced to 2.8mm, while maintaining good operational performance. It is important to note that the choice of technology should be based on a comprehensive assessment. For airway entrapment foreign bodies, rigid bronchoscopy may have more advantages; for peripheral small foreign bodies, flexible or fiberoptic bronchoscopy is more suitable. Medical institutions should choose the most appropriate treatment plan based on the specific conditions of the child, the characteristics of the foreign body, and the technical conditions.

Overall, the three bronchoscopy techniques have their applicable scenarios, but the electronic bronchoscope from Mole Medical demonstrates outstanding comprehensive advantages in pediatric patients. Its flexible operation performance, lower trauma risk, and good anesthesia adaptability make it the preferred technique for bronchial foreign body removal in pediatrics. With continuous technological progress, flexible bronchoscopy is expected to play a more important role in the diagnosis and treatment of respiratory diseases in children.
Categories
Latest Articles
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipiscing elit. Quisque faucibus ex sapien vitae pellentesque sem placerat. In id cursus mi pretium tellus duis convallis. Tempus leo eu aenean sed diam urna tempor. Pulvinar vivamus fringilla lacus nec metus bibendum egestas. Iaculis massa nisl malesuada lacinia integer nunc posuere. Ut hendrerit semper vel class aptent taciti ... Read more
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipiscing elit. Quisque faucibus ex sapien vitae pellentesque sem placerat. In id cursus mi pretium tellus duis convallis. Tempus leo eu aenean sed diam urna tempor. Pulvinar vivamus fringilla lacus nec metus bibendum egestas. Iaculis massa nisl malesuada lacinia integer nunc posuere. Ut hendrerit semper vel class aptent taciti ... Read more

MoleMedical Shines at WHX Dubai 2026: Showcasing Full Range of Medical Endoscopes & Forging Global Partnerships
The 51st World Health Expo Dubai (WHX Dubai 2026), formerly known as Arab Health, concluded successfully after a four-day showcase from February 9 to 12, 2026, at the Dubai Exhibition Centre (DEC) . As a leading global event in the medical device industry, this year’s exhibition welcomed over 4,300 exhibitors and 235,000 professional visitors from ... Read more

How to Choose a Reliable Video Laryngoscope Partner? MoleMedical Empowers Airway Safety with Technical Expertise & Clinical Validation
In critical moments of emergency and intensive care, the video laryngoscope is essential for securing the airway – a procedure where performance directly dictates resuscitation success and patient outcomes. Faced with significant technical variations among equipment suppliers, healthcare institutions require a rigorous evaluation framework. Three dimensions are non-negotiable: Technical Autonomy, Clinical Efficacy, and Service Responsiveness. ... Read more

How to Choose the Best Flexible Bronchoscope Manufacturer? Three Key Dimensions Highlight Mole Medical’s Core Advantages
n respiratory intervention diagnostics, the performance of flexible bronchoscopes directly impacts early lung cancer detection and emergency response success. Facing diverse manufacturers, healthcare institutions should prioritize three critical dimensions: technological autonomy, clinical adaptability, and infection control capabilities. Jiangsu Mole Medical Technology Co., Ltd. has earned global trust through its full-chain R&D capabilities, clinical validation across ... Read more



