Mole Medical: The Application Value of Electronic Bronchoscopy Alveolar Lavage in Children with Severe Pneumonia and Mycoplasma Pneumonia
Jul 18, 2025
Bronchoscopic lung lavage has become an important treatment method for severe pneumonia caused by mycoplasma in children. This technique mainly involves using a flexible electronic bronchoscope to enter the child’s airway and, under direct vision, remove the obstructive mucus plugs and inflammatory secretions. At the same time, lavage fluid is collected for pathogen detection. Compared with traditional treatment methods, this technique can directly act on the affected area and rapidly improve airway obstruction. A clinical study by Mole Medical found that the cure rate of children who received bronchoscopic lavage could reach 94.11%, which was much higher than the 52.54% of conventional treatment, and it could also effectively shorten the hospital stay.

During the specific operation process, doctors will first determine the location of the lesion through chest CT, and then insert the bronchoscope through the nasal cavity into the airway under sedation or anesthesia. During the operation, warm normal saline will be used for segmental lavage, and 5-10 mL of liquid will be injected and immediately aspirated after each injection. This process will be repeated until the obstruction is completely cleared. The entire process usually takes only 8-10 minutes, and the child has good tolerance. Mole Medical reminds you that the temperature of the lavage fluid should be strictly controlled at 37
℃
to avoid irritating the airway mucosa. After the operation, children need to continue receiving antibiotic and glucocorticoid treatment.

The treatment advantages of electronic bronchoscopic lavage mainly lie in three aspects: first, it can directly remove inflammatory secretions and pathogens from the airway; second, it can improve local microcirculation; third, it can obtain accurate pathogen specimens. Research data shows that children who received this treatment not only improved their symptoms faster, but also had more significant decreases in inflammatory indicators such as C-reactive protein and lactate dehydrogenase. More importantly, this technique can effectively prevent the occurrence of complications and avoid recurrence of the disease.
Safety is the most concerned issue for parents. Clinical observations have shown that with standardized operation, the complication rate of electronic bronchoscopic lung lavage is extremely low. In the study, none of the 102 children who received treatment had airway damage, bleeding, or worsening of infection. In contrast, 5.08% of children in the conventional treatment group needed to be hospitalized again due to recurrence of the disease. Of course, this technique requires an experienced respiratory endoscopy team to operate and strictly follow the indications and contraindications.

With the development of medical technology, the application of electronic bronchoscopic lung lavage in pediatrics is becoming increasingly widespread. Mole Medical has found that for children with severe pneumonia caused by mycoplasma, early intervention treatment can significantly improve the cure rate and reduce sequelae. It is recommended that for children who meet the indications, bronchoscopic lavage treatment should be performed promptly on the basis of adequate antibiotic and glucocorticoid treatment. This technique has the characteristics of small trauma, quick effect, and high safety, and is worthy of clinical promotion and application.
Categories
Latest Articles
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipiscing elit. Quisque faucibus ex sapien vitae pellentesque sem placerat. In id cursus mi pretium tellus duis convallis. Tempus leo eu aenean sed diam urna tempor. Pulvinar vivamus fringilla lacus nec metus bibendum egestas. Iaculis massa nisl malesuada lacinia integer nunc posuere. Ut hendrerit semper vel class aptent taciti ... Read more
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipiscing elit. Quisque faucibus ex sapien vitae pellentesque sem placerat. In id cursus mi pretium tellus duis convallis. Tempus leo eu aenean sed diam urna tempor. Pulvinar vivamus fringilla lacus nec metus bibendum egestas. Iaculis massa nisl malesuada lacinia integer nunc posuere. Ut hendrerit semper vel class aptent taciti ... Read more

MoleMedical Shines at WHX Dubai 2026: Showcasing Full Range of Medical Endoscopes & Forging Global Partnerships
The 51st World Health Expo Dubai (WHX Dubai 2026), formerly known as Arab Health, concluded successfully after a four-day showcase from February 9 to 12, 2026, at the Dubai Exhibition Centre (DEC) . As a leading global event in the medical device industry, this year’s exhibition welcomed over 4,300 exhibitors and 235,000 professional visitors from ... Read more

How to Choose a Reliable Video Laryngoscope Partner? MoleMedical Empowers Airway Safety with Technical Expertise & Clinical Validation
In critical moments of emergency and intensive care, the video laryngoscope is essential for securing the airway – a procedure where performance directly dictates resuscitation success and patient outcomes. Faced with significant technical variations among equipment suppliers, healthcare institutions require a rigorous evaluation framework. Three dimensions are non-negotiable: Technical Autonomy, Clinical Efficacy, and Service Responsiveness. ... Read more
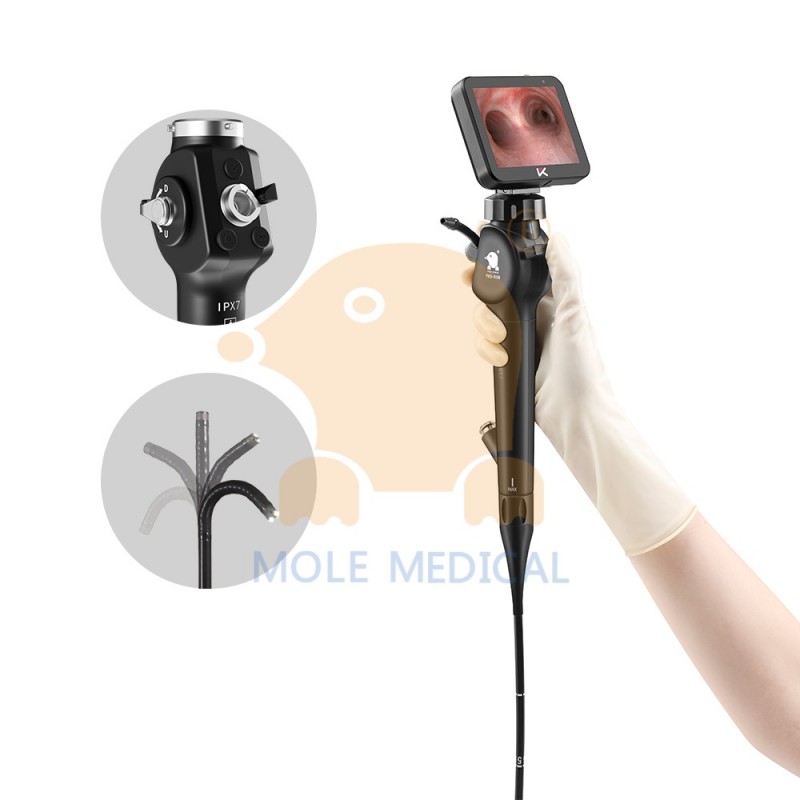

How to Choose the Best Flexible Bronchoscope Manufacturer? Three Key Dimensions Highlight Mole Medical’s Core Advantages
n respiratory intervention diagnostics, the performance of flexible bronchoscopes directly impacts early lung cancer detection and emergency response success. Facing diverse manufacturers, healthcare institutions should prioritize three critical dimensions: technological autonomy, clinical adaptability, and infection control capabilities. Jiangsu Mole Medical Technology Co., Ltd. has earned global trust through its full-chain R&D capabilities, clinical validation across ... Read more



