How to use anesthesia laryngoscopy?
Sep 04, 2023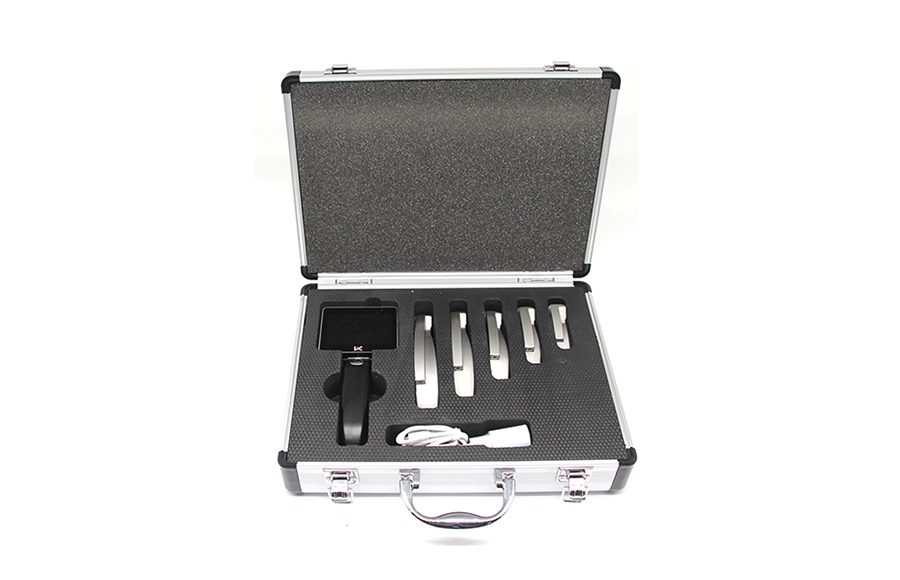
1.Direct anesthesia laryngoscopy is performed under mucosal surface anesthesia. The surgeon holds the mirror in his left hand and protects the upper teeth with thick gauze…
Anesthesia laryngoscopy
1.Direct laryngoscopy is performed under mucosal surface anesthesia. The surgeon holds the mirror in his left hand and protects the upper teeth with thick gauze. The mirror is introduced into the mouth along the back of the tongue and transferred deep into the midline, to the base of the tongue. The thumb and index finger of the right hand assist in holding the tube from front to back when the epiglottis is seen from the laryngoscope. Tilt the proximal end of the laryngoscope up (tilted forward when sitting) and the distal end toward the back of the pharynx without touching it. Continue into the lens beyond the free edge of the epiglottis. After seeing the epiglottis tubercle, lift the laryngoscope with the left hand with a parallel upward force, and press the epiglottis to fully lift it to expose the larynx. At this time, if laryngospasm occurs, the glottis is closed and the glottis cannot be seen.
2.The laryngoscope should be fixed in place, and the laryngeal image can be seen after the laryngospasm touches for a moment. If the laryngoscope touches the mucosa of the laryngeal cavity too deeply to cause spasm of the arch reflex, the laryngoscope should be slightly retracted for observation, and the subject should be told to make the sound of “clothes” and observe the movement of the vocal cords. At this time, the surgeon can perform various necessary operations with the right hand.
3.If the subject’s neck is short and thick, and the anterior commissure of the vocal cords is not easily exposed, the head must be raised, the left hand lifts the laryngoscope up, the right thumb presses the laryngoscope up from the bottom, and the remaining fingers of the right hand should be fastened on the patient’s right upper The teeth are supported in unison to lift the epiglottis. If this approach is unsuccessful, you can ask your assistant to compress the thyroid cartilage down or use a combined laryngoscopy instead. An anterior arthrolaryngoscope not only provides a clear view of the anterior vocal fold joints, but can also be inserted into the glottic fissure to examine the subglottic space.
4.When examining young children, in order to prevent laryngeal edema after this operation, the tip of the laryngoscope should not compress the epiglottis, and the base of the tongue should only be lifted forward, and the epiglottis will stand up to expose the larynx.
5.Complications of anesthesia laryngoscopy
It usually happens rarely. Children, especially those with spasticity, may develop severe, life-threatening laryngospasm during surgery. During the operation, the movements should be as gentle as possible to reduce the damage to the throat mucosa and reduce the chance of hematoma, bleeding or bleeding secondary to infection.
Latest Articles

MoleMedical to Showcase Full-Scope Visualized Endoscopy Solutions at CMEF Shanghai Spring 2026
Jiangsu MoleMedical Electronics Technology Co., Ltd. is pleased to announce its participation in the 93rd China International Medical Equipment Fair (CMEF), Spring 2026, in Shanghai. As a leading innovator specializing in endoscopic visualization technologies, we extend a warm invitation to global medical professionals, distributors, and industry partners to visit our booth and explore our comprehensive solutions ... Read more

MoleMedical Shines at WHX Dubai 2026: Showcasing Full Range of Medical Endoscopes & Forging Global Partnerships
The 51st World Health Expo Dubai (WHX Dubai 2026), formerly known as Arab Health, concluded successfully after a four-day showcase from February 9 to 12, 2026, at the Dubai Exhibition Centre (DEC) . As a leading global event in the medical device industry, this year’s exhibition welcomed over 4,300 exhibitors and 235,000 professional visitors from ... Read more

How to Choose a Reliable Video Laryngoscope Partner? MoleMedical Empowers Airway Safety with Technical Expertise & Clinical Validation
In critical moments of emergency and intensive care, the video laryngoscope is essential for securing the airway – a procedure where performance directly dictates resuscitation success and patient outcomes. Faced with significant technical variations among equipment suppliers, healthcare institutions require a rigorous evaluation framework. Three dimensions are non-negotiable: Technical Autonomy, Clinical Efficacy, and Service Responsiveness. ... Read more

How to Choose the Best Flexible Bronchoscope Manufacturer? Three Key Dimensions Highlight Mole Medical’s Core Advantages
n respiratory intervention diagnostics, the performance of flexible bronchoscopes directly impacts early lung cancer detection and emergency response success. Facing diverse manufacturers, healthcare institutions should prioritize three critical dimensions: technological autonomy, clinical adaptability, and infection control capabilities. Jiangsu Mole Medical Technology Co., Ltd. has earned global trust through its full-chain R&D capabilities, clinical validation across ... Read more

Disposable Nephroscopes: Redefining Safety & Efficiency in Urology
Introduction The shift towards minimally invasive urological surgery has found a pivotal ally: the disposable nephroscope. As traditional reusable scopes grapple with persistent biofilm contamination risks and soaring sterilization costs, the global medical community is rapidly adopting single-use solutions. This article analyzes the clinical value, technological evolution, and dynamic innovation landscape driving this transformative shift. ... Read more



